The development of products and services that genuinely address human needs strongly relies on actionable design research—it’s a vital backbone of good user experience that ensures optimal usability and increased user satisfaction. As a result, leading impressive returns and a larger market share for organizations.
Despite its benefits, design research is often neglected by businesses, often due to the fact, few people understand its value outside the design department.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the fundamentals of design research, when it should be conducted, common methods, and how it can benefit a product when thoughtfully applied.
Let’s get right into it.
What is Design Research?
Design research is a customer-focused framework of research methods that allows you to uncover:
Who your users are;
The problems they’re facing;
The way in which they’ll be using your product;
Qualitative and quantitative research methods provide designers with a better understanding of a product’s requirements, as well as the more minor details regarding user needs. As a result, this enables them to create better and more satisfying products.
Why Do You Need It?
Let’s take a quick look at the benefits that design research can provide you with.
To Learn Consumer Behavior
In order to create products that fit your users’ behavior, you need to start with understanding their behavior in the first place. Design research allows teams to acquire an in-depth understanding of their users’ expectations and usage contexts, which helps them better understand the product requirements.
After all, communicating with the people you’re designing for helps you develop a sense of empathy and care for their needs and desires, enabling you to make quicker and more informed decisions on a regular basis.
To Uncover Actionable Insights
One of the most complicated things designers do is translate raw qualitative and quantitative data into graphic experiences. Things as straightforward as logos can take weeks of research and ideation before they reach a certain degree of market fitness.
Conducting in-depth research allows designers to extract actionable insight, thus making it easier for them to navigate needs and craft interfaces that fit a user’s persona with high accuracy.
To Keep Irrationality at Bay
There is a wide array of biases humans are subject to; many are extremely harmful to good design. For instance, we assume that human behavior is rational and easily predictable—it’s not. There’s a growing body of research and literature that explores the irrationality of human decision-making, especially when being asked to explain their decisions. We often operate in partly deterministic ways, but there are also plenty of variables in the choices we make that introduce a lot of spontaneity. Basically speaking, it’s hard to understand people—we often don’t really understand ourselves.
More importantly, making assumptions about the things that surround us is a skill we developed throughout evolution that, unfortunately, has a flip side. While this was an incredibly useful adaptation we’ve made to survive in prehistoric times, this trait is becoming increasingly cumbersome today—while still critical for our survival, it often pushes us to make erroneous conclusions about people, cultures, and even design needs.
Design research is a valuable tool that allows designers to remember that they are not their users, allowing them to create better and more useful experiences.
To Get a Greater Bottom Line for Less Money
While a designer’s gaze should always be pointed to their users’ experience, business goals are no less of a responsibility. But there’s a catch—while UX on its own has a stellar ROI, higher management should be open to investing in activities such as design research to help user experience specialists deliver truly impressive returns. While research does cost money, the value it yields, as a result, makes the initial investment appear insignificant.
When Should You Conduct Research?
Typically, most design research is conducted during the empathize and prototype phases, both to inform design decisions and test them with end-users.
Adding New Features
Complementing a new product with additional features isn’t necessarily as straightforward as it may appear and can often require many person-hours of research work. Typically, introducing a new feature should be preceded by thorough market and user research to understand how your competition chooses to design identical features and how these solutions can be improved upon.
Redesign
Successful redesigns are supposed to be data-driven. If you choose to change your brand’s and product’s appearance and thus invest lots of money into this, you should have conducted extensive research in order to meet your users’ and customers’ expectations.
Similarly, redesigns should ideally come with lots of usability and A/B testing in order to continuously tailor the new product to fit the needs of the people it’s designed for.
Create a New Design
Creating a product from scratch should always involve extensive research. First off, it provides a better understanding of which features should be prioritized and what product areas should focus on.
While it doesn’t sound like a critical step in product development, it’s important to underline that designers typically don’t and generally shouldn’t create experiences that satisfy their subjective preferences or those of the stakeholders. A prototype should first and foremost meet the needs of its users and take into account the context in which it will be used.
Attract New Audience
Research is a valuable tool if you’re looking to expand your product in new geographies or a new target audience. To better understand how a new persona or market segment should be catered to, businesses can explore a wide array of techniques ranging from surveys and interviews to test usability and beyond.
Investing some time into learning more about your new potential audience’s habits, needs, and aspirations, will invariably allow you to create better and more efficient strategies that will fast track your product to success.
Understand a Product’s End-to-End Lifecycle
Research mustn't be limited to particular areas of a product’s lifecycle. Every single phase of the process can significantly benefit from studying and exploring the market and its opportunities.
User experience is about creating “good enough“ products and committing to continuously improving them. It’s critical to keep in mind that perfection is unattainable and that there’s always a reasonable amount of optimization that can be done. Given that any product exists in an ever-changing market, there are always new challenges that should be addressed in order to keep it on or above par with its competition.
Methods of Design Research
Now that we’ve looked into the value that design research brings to the table, let’s take a quick look at some research methods.
User Interviews
User interviews are probably the most conceptually straightforward research method out there. Think about it—making a successful product is all about meeting people’s needs. Setting up an interview with a potential customer and asking them what they actually want is probably the most evident way to empathize and try to understand their perspective.
This is specifically why user interviews are such an invaluable part of designing a successful product. Of course, not all of them are unstructured, and there are plenty of principles to keep in mind when you're figuring out what and how to ask. Still, this method is probably one of the most rewarding in terms of return of time and effort invested.

Case Study Design
This is a type of study that focuses on a very narrow topic rather than delving into a statistical exploration. Typically, case studies are used to zoom in on a very specific part of a body of research and present it as one researchable topic.
Exploratory Design
This type of study is typically used when a particular issue hasn’t been studied very thoroughly in the past. An exploratory approach allows researchers and designers to gather a better understanding of the problem at hand rather than generate immediate actionable solutions.
Observational Research Design
People provide plenty of reasons for why they chose to do or not do something, but their explanations aren’t always accurate. That is not to say that we shouldn’t listen to them at all and instead shove our solutions down their throats and have them figure things out. We should take anything said in an interview with a grain of salt—and that grain of salt should come in the form of observational studies.
To truly understand why people do the things they do, we should observe their actions, aside from simply asking them about their rationale.
Descriptive Research Design
This is a very useful quantitative research method that aims to narrow down a particular phenomenon and gather information about it until it’s confidently understood. Typically, this type of study is very detailed and systematic. Their main goal is to describe, observe, and extract conclusions from it.
Longitudinal Studies
This type of study revolves around correlation research. The main idea behind them is to study phenomenons and events throughout a longer period of time. Compared to a user interview that can last one or two hours, longitudinal studies can analyze variables anywhere from weeks and months to decades.
These studies are essential when it comes to uncovering correlations or causality between two or more variables, which can provide you with extremely valuable actionable insight.
Surveys and Questionnaires
These methods are easily among the most efficient ones—there isn’t too much time invested and there’s plenty of information gathered. Of course, it’s worth mentioning that there’s only so much control over the answers you’re going to get, given that your participation is extremely limited here, but still, it’s an extremely useful way to lay the groundwork for more in-depth studies.
Surveys and questionnaires are extremely useful in situations where you have a very diverse group of users.
Card Sorting
Card sorting is a critical research method when it comes to understanding the optimal information architecture of a website or app. Typically, these sessions revolve around potential users organizing topics into broader categories in an attempt to understand the way they perceive relationships between individual topics.
There are multiple types of card sorting exercises and software that will come in handy depending on the situation you’re in.

Usability Testing
Basically speaking, usability testing allows you to understand how easy-to-use and intuitive a piece of design is for your target users. Typically, these tests revolve around providing people with tasks and observing them during their attempts. This method is very useful before product release and is normally conducted multiple times to allow you to see how the changes in a prototype affect the usability of the product.
Contextual Inquiry
This research method is very useful in the early phases of the design process, specifically in the discovery phase. It allows designers to navigate the project better by understanding the requirements, features, personas, content strategy, and so forth.
Overcoming Challenges in Design Research
Design research, while invaluable, often faces hurdles that can hinder its effectiveness. In this section, we consider significant challenges that you must consider and how to mitigate them.
Time and Budget Constraints
To maximize the impact of design research within limited resources, consider the following strategies:
Prioritizing Research Efforts:
Focus on critical areas: Identify the most pressing questions and focus research efforts on those areas.
Set clear objectives: Define specific research goals to avoid scope creep and ensure efficient resource allocation.
Efficient Research Methodologies:
Rapid prototyping: Quickly iterate on design concepts to gather user feedback.
Remote user testing: Conduct usability tests remotely to reduce costs and time.
Leveraging Existing Data and Insights:
Analyze user analytics and customer support data.
Review previous research reports and case studies.
Conduct literature reviews to identify relevant research findings.
Resistance to Change
Another common challenge in design research is resistance to change from stakeholders. To overcome this, consider these strategies:
Building Strong Relationships with Stakeholders:
Establish open and honest communication channels.
Build trust and credibility through consistent delivery.
Involve stakeholders in the research process to gain their buy-in.
Communicating the Value of Design Research:
Highlight the positive impact of design research on business outcomes.
Use case studies and metrics to demonstrate ROI.
Tailor your communication to the specific needs and interests of each stakeholder.
Using Data-Driven Decision-Making:
Present data-backed insights to support design decisions.
Use visual aids to make data more accessible and understandable.
Encourage a data-driven culture within the organization.
Ethical Considerations in Design Research
Ethical considerations are necessary in design research, particularly when you are dealing with human participants. User privacy, informed consent, and transparency throughout the research process are factors you must consider.
To ensure ethical conduct, researchers should:
Obtain informed consent: Clearly communicate the purpose of the research, potential risks and benefits, and the participant's right to withdraw at any time.
Protect user privacy: Anonymize and aggregate data to safeguard participant identity.
Ensure data security: Implement robust measures to protect sensitive information.
Avoid deceptive practices: Be honest and transparent about the research process.
Consider the impact of the research: Evaluate the potential social and environmental consequences of the design solutions.
It's easier for researchers to build trust with participants and ensure the integrity of their work by adhering to these ethical principles.
Emerging Trends in Design Research
As technology advances and user needs change, the field of design research will continuously evolve. One of the most significant trends is the increasing integration of AI-powered tools and techniques.
AI-Powered Design Research
As we have already witnessed, AI can greatly simplify and improve design research by accessing and processing data in ways far more efficient than humans. Here are key impact areas:
Automated Data Analysis: AI data analysis tools can efficiently process large datasets, identify patterns, and extract meaningful insights. This frees up researchers to focus on higher-level analysis and interpretation.
Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical data and current trends, AI can forecast future user behaviors and preferences. This enables researchers to make informed decisions and anticipate user actions.
AI-Generated Design Concepts: AI-powered tools like UX Pilot can generate creative design ideas based on specific requirements. While human designers are still essential for critical thinking and problem-solving, AI can provide inspiration much faster.
Remote and Distributed Research
The rise of remote work has led to the adaptation of design research methodologies to accommodate virtual collaboration.
Virtual Usability Testing: Remote usability testing allows researchers to observe users interacting with designs in real-time, regardless of their physical location.
Remote User Interviews: Conducting interviews via video conferencing tools enables researchers to connect with participants from around the world.
Collaborative Tools for Remote Teams: Collaborative tools like Miro, Figma, and Slack facilitate seamless communication and shared workspaces for distributed design teams.
Design Research for Sustainability
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in design, there’s an increasing emphasis on creating products and services that minimize environmental impact.
Eco-friendly Design Principles: Designing products that prioritize resource efficiency, reduce waste, and minimize energy consumption.
Sustainable Materials and Processes: Selecting materials with low environmental impact and adopting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Measuring the Environmental Impact of Design Decisions: Assessing the carbon footprint, water usage, and waste generation associated with design choices.
Advanced Research Methodologies
Want to take design research to the next level? Here are more advanced techniques.
Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research involves immersing oneself in a particular cultural setting to gain a deep understanding of people's behaviors, beliefs, and values. This qualitative research method is particularly useful for understanding complex user behaviors and identifying unmet needs.
Immersive Field Research: Spending extended periods of time in the field to observe and interact with participants in their natural environment.
Participant Observation: Actively participating in the activities of the target group to gain firsthand insights.
Cultural Analysis: Analyzing cultural artifacts, symbols, and practices to understand the underlying meanings and values.
Diary Studies
Diary studies involve asking participants to record their experiences and behaviors over a specific period. This method provides rich, detailed data about user behavior patterns and helps identify pain points and opportunities for improvement.
Long-term User Tracking: Monitoring user behavior over extended periods to identify trends and patterns.
Understanding User Behavior Patterns: Analyzing diary entries to gain insights into how users interact with products and services.
Identifying Pain Points and Opportunities: Identifying areas where users encounter difficulties or express dissatisfaction.
Heuristic Evaluation
Heuristic evaluation is a usability inspection method that involves UX experts evaluating a user interface against a set of usability principles. This method can be used to identify potential usability issues and design flaws early in the design process.
Expert Review of User Interfaces: Assessing the design of user interfaces against established usability guidelines.
Identifying Usability Issues and Design Flaws: Pinpointing areas where the design may be confusing, inefficient, or error-prone.
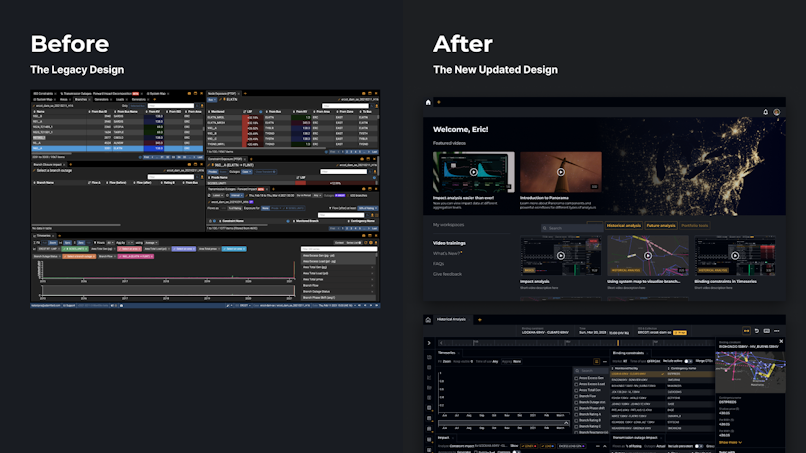
Case Study: Marginal Unit
For Marginal Unit, a provider of grid congestion modeling and analytics software, in-depth design research was pivotal to addressing their complex UX challenges. Our approach combined usability sessions, prototype testing, stakeholder interviews, and information architecture workshops. These efforts provided deep insights into user needs and the energy market, guiding our design decisions that ended up transforming the platform.
Key Outcomes
Validated new features through iterative research.
Created a prioritized UX improvement roadmap.
Revamped information architecture and UX artifacts to reflect user behavior.
Developed a scalable design system for streamlined development.
Struggling with high churn rates or unhappy users? We can help you like we did with Marginal Unit. Book a free consultation to discuss with our experts.
Visualizing Design Research Insights
At some crucial point, you will have to communicate findings to stakeholders and make data-driven decisions. This is where effective data visualization techniques and tools come in.
Data Visualization Techniques
Infographics: Visually appealing representations of complex data, such as user flows, user personas, and statistical findings.
Dashboards: Interactive tools for monitoring key metrics and trends over time.
Data Maps: Visualizing geographic data to identify patterns and correlations.
Storyboarding
Storyboarding is a powerful technique for visualizing user journeys and interactions. By creating a sequence of frames, designers can:
Visualize user journeys: Map out the steps a user takes to complete a task.
Communicate design concepts: Present design ideas to stakeholders in a clear and concise way.
Prototyping
Prototyping is an essential part of the design process. It involves creating tangible representations of design concepts to test and refine ideas.
Low-fidelity prototyping: Simple, low-cost prototypes, such as paper sketches or wireframes.
High-fidelity prototyping: Detailed, interactive prototypes that closely resemble the final product.
Interactive prototypes: Prototypes that allow users to interact with the design, providing valuable insights into usability and user experience.
The bottom line
In order to create a product that actually meets user needs and improves their lives, we need to be able to interact with them and have them provide us with feedback. Unfortunately, designers and stakeholders sometimes make erroneous assumptions about the people they’re developing products for, and an important part of letting go of these assumptions is letting users be the experts.
Design can be challenging, odd, and ambiguous at times. However, that should never stop us from continuously finding food for thought and brilliant solutions as a result of it. Research is not something businesses can disregard—it’s one of the few surefire ways to ensure that they’re not designing the wrong thing.