Ideas are the currency of life. Being able to generate high-quality ideas will most certainly have a powerful effect on your products' quality and, arguably, your life.
We often hear romantic stories about business people or scientists waking up one morning with a genius idea, which they’ve then leveraged to produce groundbreaking work. Unfortunately, this isn’t how things typically work.

Hire a World-Class Product Design Agency
Let us help your skyrocket your activation, conversion & retention.
Contact usWhen it comes to product design, we can’t rely on “Eureka” moments to guide design work. Effective ideation demands a structured and methodical approach, which is precisely what this article is about.
Let’s dive right in, shall we?
So, What is Ideation?
Ideation is an essential process that UX designers, and product people in general, use to generate a broad spectrum of valuable ideas that can then be used to fuel the design process. Its central goal is to explore a wide array of thoughts and concepts that can be applied to form or augment a product.
A well-conducted ideation session will provide the product team with a robust foundation for prototypes and ensure that all the viable options have been considered.

Why is Ideation Important?
Ideation isn’t just a helpful trick designers use to make products a little better. By tapping into this process early into the product design process, you’ll be able to address a host of potential issues, making your operations more efficient and cost-effective.
Here are a few significant benefits that ideation grants us:
An innovative and user-centric approach to design by addressing your users’ immediate needs;
An outside-the-box thought process that enables the team to go beyond the most obvious solutions;
Alignment across team members by ensuring a coherent strategy and vision;
A wealth of creative solutions that broaden design opportunities, allowing to develop products with maximum efficiency;
The Grand Scheme of Things
Ideation is the third stage of the Design Thinking process — this is where the product team lays the groundwork for innovation and problem-solving. It’s preceded by the Empathize and Define stages that allow achieving a better understanding of the end-users and define product goals.
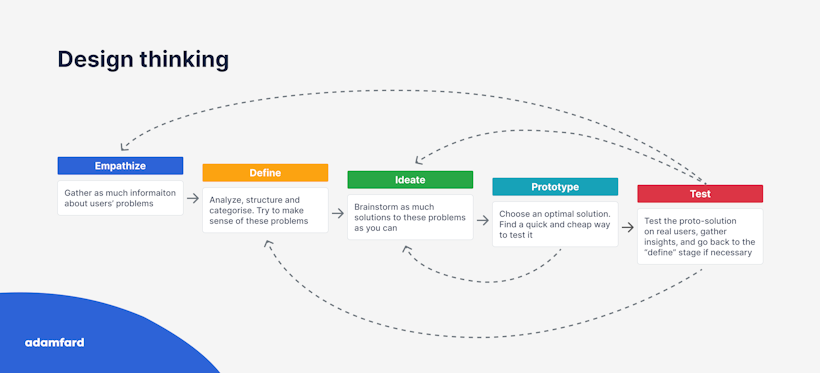
During the Empathize stage, designers develop a sense of empathy for customers, allowing them to understand and contextualize their experiences, fears, and motivations.
The Define stage, on the other hand, allows designers to assemble and analyze the data collected during the Empathize stage. This enables them to outline the central issues that a team has identified so far.
Ideation aims to build on the findings of the previous stages. It is when teams leverage their empathy for users and their design skills to solve the problems they’ve uncovered in the Define stage.
The empathy and definition stages exist for a good reason. Therefore, we wouldn’t advise diving right into brainstorming or other ideation activities without having your research done. If you do, you might end up ideating solutions for multiple problems at once, or a problem that isn’t actually one. Either way, it’s not the best use of your time.
How to Ideate Efficiently
In order for ideation sessions to be as efficient as possible, there is a variety of principles that need to be taken into account:
Although it may seem counter-intuitive, it’s essential to focus on quantity over quality. The more ideas your team can generate — the better;
It’s also essential not to criticize any ideas. Criticism has its time and palace in Design Thinking, but due to the focus on quantity, it’s best to abstain from disqualifying potential solutions at this time;
The more, the merrier. In order to broaden the spectrum of potential solutions, it’s always good to involve more people in the ideation process;
Challenge yourself and your team to think outside the box, regardless of how unreasonable some ideas may seem;
Make sure to save all the ideas in a live document. Having them visible will allow to leverage them for more inspiration;
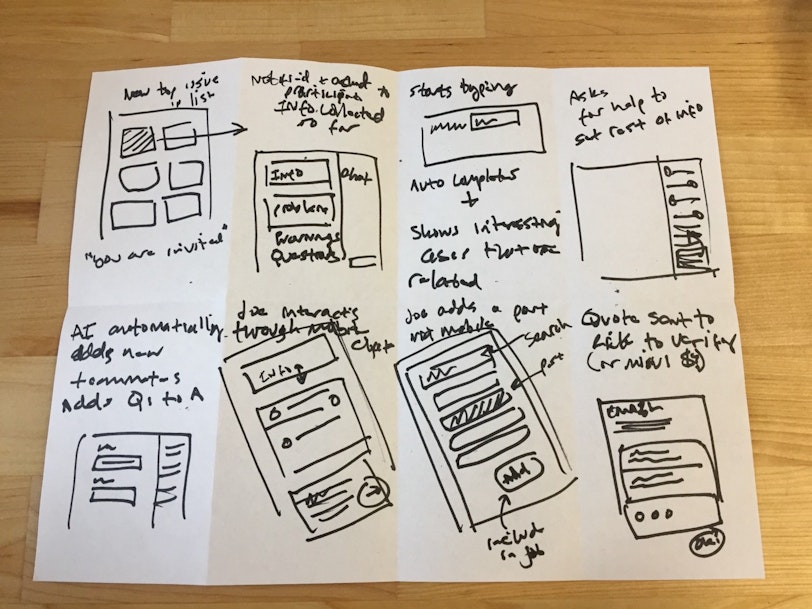
It’s important to underline that ideation can be applied in a variety of ways and for a multitude of scenarios. Whether it’s creating an additional feature for your product, rethinking tone of voice, or making changes to user journeys — this process will always serve as an invaluable tool.
Long story short, ideation, and design thinking in general works for problems that have a potential array of solutions (unlike a puzzle that usually only has one).
Tools, Tips, and Tricks
There are lots of things that can assist you with running fruitful ideation sessions. Here are a few of them:
Make use of post-it notes. They’ll be convenient during offline sessions. The limited space a sticky note offers also helps write ideas clearly and not get stuck with the details;
Try out Miro or FigJam — these are one of the best tools for ideation and remote workshops. The learning curve is fairly manageable, even for people who aren’t exactly tech-savvy. Ideation workshops aside, Miro is a great addition to your company’s digital tool kit;
Ideally, it would help if you had a moderator who would guide the participants through the workshop. The moderator will make the process smoother by explaining the rules and keeping activities in order. In startups and other digital projects, the UX team usually takes on this responsibility;
If that’s a remote ideation session, most of which in 2021 are, insist that the participants turn on their camera. If you don’t, the temptation to check emails, Instagram feed, or browse mindlessly through the phone might get the better of your team. You need your teammates engaged and invested in the process, or else you’ll end up exploring the surface-level solutions only;
Take a deep dive into ideation techniques. A notable one is the Crazy 8’s — take an A4 sheet of paper, fold it into eight rectangles or simply draw them. Sketch 8 different ideas or solutions in 8 minutes (1 minute per idea). There’s plenty more, find one that works best for your team;
Ditch limitations — feel free to explore options that don’t seem feasible at this time due to technical limitations. Although limitations might sometimes fuel creativity, don’t get caught up in overthinking and overanalyzing. Whatever your brain produces is good enough to document;
Lastly, at the end of the workshop go over each idea and make sure the whole team understands it. The next day after the workshop, you will 100% forget the context of some of the notes and their meaning as such. That’s why clarity is vital. Rephrase or flesh out the ideas that are likely to cause confusion further down the road.
What’s Next?
Once your workshop has been conducted, it’s always a good idea to take a break and let your mind detach from the ideation process for a bit. This will allow you and your team to have a more objective perspective on the generated ideas and evaluate them fairly.
A rested mind is more conducive to proper decision-making and a careful assessment of ideas. Once you’re done with rest and recuperation, it’s time to structure the chaos that most good ideation workshops are.
Here are a few more things that will help you select the most useful ideas from the list:
Group similar ideas and merge identical ones;
Select the ones that make the most practical sense;
Try voting ideas into or out of your shortlist if opinions vary;
If facing issues with voting, consider coming up with categories like "ease", "impact", "cost", etc. and evaluating each idea with respect to a given category. This could even go as far as assigning different coefficients to each category. You can then add up the scores in each category to shortlist the best ideas;
Think of the least expensive and easy way to test the shortlisted ideas;
Keep following the Design Thinking process;
Brainstorming Techniques: A Creative Toolkit
Brainstorming is a fundamental technique in the ideation process. It involves generating a large number of ideas in a short period, often within a group setting.
Brainstorming can lead to innovative and creative solutions by encouraging a free flow of thoughts.
Here are some popular brainstorming techniques to spark your creativity:
Mind Mapping: Think of it as a visual brainstorm. You start with a central idea and branch out into related concepts. It's a great way to see connections and spark new ideas.
Freewriting: Just let your thoughts flow onto the page. Don't worry about grammar or structure. The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible, no matter how crazy they may seem.
SCAMPER: This technique is like a creative checklist. Ask yourself: "How can I Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to Another Use, Eliminate, or Reverse this idea?" It's a great way to think outside the box.
Expanding Your Ideation Toolkit: Design Sprints and SWOT Analysis
In addition to traditional brainstorming techniques, consider these powerful methods to enhance your ideation process:
Design Sprints
A design sprint is a time-boxed, collaborative approach to solving design challenges. It's a structured process that involves a diverse team working together to define a problem, ideate solutions, prototype, and test.
These sprints follow a structured timeline and can accelerate the ideation phase, leading to faster product development.
How to Apply Design Sprints to Ideation
Understand the Challenge: Clearly define the problem or opportunity you want to address.
Sketching and Ideation: Generate a wide range of ideas through sketching and brainstorming exercises.
Decision-Making: Prioritize ideas based on feasibility and potential impact.
Prototype and Test: Create low-fidelity prototypes to test ideas with users.
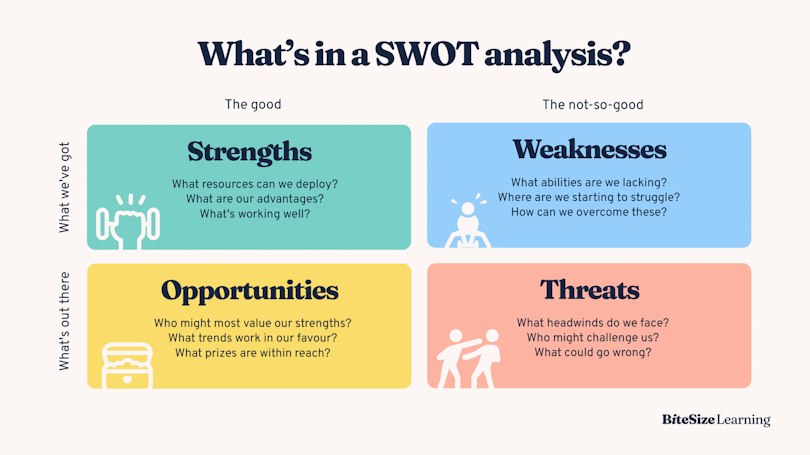
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning technique used to help a person or organization identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to business competition or project planning.
How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis for Ideation
Strengths: Identify the internal strengths of your team or organization.
Weaknesses: Recognize internal limitations or areas for improvement.
Opportunities: Explore external factors that could benefit your project.
Threats: Identify potential external challenges or risks.
By combining these techniques with traditional brainstorming, you can create a robust ideation process that leads to innovative and effective solutions.
Overcoming Ideation Challenges
While ideation is a powerful tool, it's not without its challenges. Most times, when designers fail to achieve expected results from ideation, it could be due to succumbing to one of these setbacks.
Here are some common hurdles and strategies to overcome them:
Common Challenges
Groupthink: When a group prioritizes harmony over critical thinking, it can stifle creativity and lead to suboptimal solutions.
Lack of Creativity: Sometimes, it can be difficult to think outside the box, especially when facing a complex problem.
Time Constraints: Limited time can restrict the depth and breadth of the ideation process.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
Now to overcome these challenges, here are some recommended techniques:
Encouraging Diverse Perspectives: Invite people from different backgrounds and expertise to participate in ideation sessions. Diverse perspectives can lead to more creative and innovative solutions.
Breaking Down Barriers to Creativity: Create a safe and supportive environment where participants feel comfortable sharing ideas without fear of judgment. Use techniques like brainstorming and mind mapping to stimulate creative thinking.
Effective Time Management: Set clear time limits for each stage of the ideation process. Use time-boxing techniques to allocate specific time slots for different activities. Prioritize ideas based on their potential impact and feasibility.
If designers learn to address these challenges by implementing effective strategies, they can maximize the potential of their ideation sessions and generate truly innovative solutions.
The Power of AI in Ideation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way we approach creative problem-solving, including ideation. With AI tools, we can enhance the quality and efficiency of our ideation processes significantly.
AI Tools for Ideation:
AI-Powered Brainstorming Tools: These tools can generate creative ideas based on specific prompts or constraints, helping to spark new thinking.
AI-Assisted Design Tools: AI-powered design tools can automate repetitive tasks, generate designs, and provide real-time feedback. For instance, with a tool like the UXPilot Wireframe Generator, you can create wireframes in seconds.
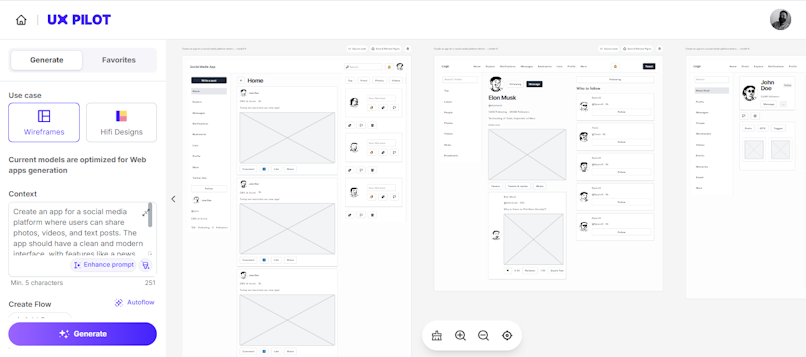
Using UXPilot to generate wireframes.
Benefits of AI in Ideation
Increased Creativity and Innovation: AI can help us think outside the box by suggesting unconventional ideas and approaches.
Faster and More Efficient Ideation Processes: AI tools can automate certain aspects of the ideation process, saving time and effort.
Data-Driven Insights: AI can analyze large datasets to identify trends and patterns, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making.
By embracing AI, we can unlock new levels of creativity and innovation in our ideation processes.
Visualizing the Ideation Process: A Picture is Worth a Thousand Words
Visualizing your ideas is a powerful way to communicate and collaborate. Visual tools can help make complex concepts more understandable and inspire creative thinking.
Creating Visual Diagrams:
Flowcharts: Map out processes and workflows to identify potential bottlenecks and optimization opportunities.
Mind Maps: Visually organize ideas and concepts, revealing connections and patterns.
Storyboards: Create visual narratives to illustrate user journeys and product experiences.
The Importance of Visual Communication
Visual communication is an indispensable tool for designers for many valid reasons. Here's why you must consider them.
Enhanced Understanding: Visuals can help you and your team grasp complex ideas more easily.
Improved Collaboration: Sharing visual representations of ideas can facilitate better communication and collaboration.
Effective Problem-Solving: Visualizing problems can help you identify root causes and develop innovative solutions.
Visual tools make it easier to bring your ideas to life, communicate them more effectively, and make better decisions.
Conclusion
Ideation is an invaluable tool in the lifecycle of any product. It’s more than simply generating ideas — it’s a way to make sure that you explore all the options available and select the most viable ones. By doing so, you’re ensuring that your product will have a robust theoretical foundation that will fuel your design decisions.
FAQ
What do you do at the ideation phase in UX?
In this phase, your task is to generate as many diverse ideas to tackle a specific problem.
What is ideation in ux?
In UX, ideation is the third stage in the design thinking process, the goal of which is to brainstorm solutions to the problems you've understood and defined.