Introduction
Imagine a world without apps. No Instagram, no TikTok, no Netflix. It's hard to picture, right? Digital products have become so ingrained in our lives that it's almost impossible to imagine a day without them. And behind every cool app or website is a team of talented designers.
Product design, in the digital world, is basically the art and science of creating digital experiences that excel. It's about making things look good and work even better. Did you know that about 70% of online businesses fail due to bad user experience?
In this comprehensive guide, we'll take you on a journey through the crucial steps involved in the product design process. We'll cover everything from the initial spark of an idea to the final launch.
So, whether you're a designer yourself or just curious about how these digital marvels come to life, let's dive in!
Step 1: Ideation and Research
Always kick off your journey by brainstorming some innovative ideas for your digital product. This is where the creativity flows.
Brainstorming Techniques
To spark inspiration and explore different possibilities, consider these effective brainstorming techniques:
Mind mapping
Visualize your thoughts and connect related ideas using a mind map. This can help you uncover hidden connections and generate new perspectives.
Brainstorming sessions
Gather a group of people and engage in a collaborative brainstorming session. Encourage open communication and free-flowing ideas.
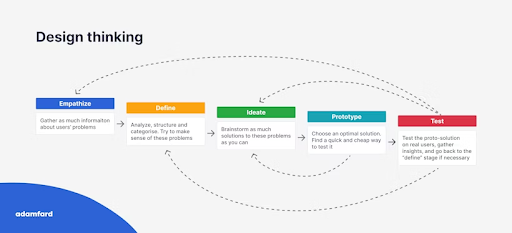
Design thinking
Adopt a human-centered approach by focusing on understanding your users' needs and desires. This will help you create products that truly resonate with them.
Market Research
Once you have a solid foundation of ideas, it's time to conduct thorough market research.
This involves understanding your target audience, analyzing competitors, and staying informed about industry trends.
Target audience
Create detailed user personas to represent your ideal customers. This will help you tailor your product to their specific needs and preferences.
Competitive analysis
Study your competitors' products to identify their strengths, weaknesses, and unique selling points. This will help you differentiate your product and offer something unique.
Industry trends
Stay up-to-date with the latest trends and developments in your industry. This will ensure that your product aligns with market expectations and remains relevant.
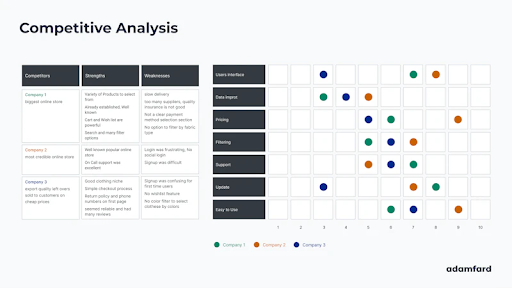
Competitive analysis example.
User Research
User research is where we get real with our users. By understanding their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, you can create a product that truly resonates with them.
User interviews
This is like having a one-on-one chat with your potential customers. Ask them questions, listen to their stories, and uncover their hidden desires. It's like a digital focus group!
Surveys
Send out surveys to a wider audience and collect valuable data. Think of it as a digital questionnaire, where you can ask specific questions and get direct feedback.
Usability testing
Watch your users interact with prototypes of your product. It's like being a fly on the wall, observing their every move and listening to their thoughts. User testing will help you identify any pain points and make improvements.
Why Competitive Analysis is Important
Spy on your competitors by analyzing their products, you can learn from their successes and failures. Here's how to do it:
Identify key competitors: Who are the big players in your industry?
Analyze their products: Take a deep dive into their features, design, pricing, and marketing strategies.
Find gaps and opportunities: Look for areas where they're falling short or where there's a need for something new.
Differentiate your product: Make your product stand out from the crowd. Find your unique selling point and showcase it to the world.
Through in-depth user research and competitive analysis, you'll be armed with the knowledge and insights needed to create a truly exceptional digital product.
Stage 2: Defining the Problem
Now that you have a bunch of ideas and a good understanding of your target audience, it's time to get to the heart of the matter: defining the problem your product aims to solve.
This is where you'll crystallize your vision and ensure that your product truly meets a need.
Problem Statement
A clear and concise problem statement is the foundation of your product. It should outline the specific issue your product addresses, the target audience, and the desired outcome.
Here's a simple formula to help you craft a compelling problem statement:
For [target audience], [problem] leads to [negative consequence]. Our solution is [product] which provides [benefit].
For example, a problem statement for a new productivity app might look like this:
"For busy professionals, juggling multiple tasks and deadlines leads to stress and decreased efficiency. Our solution is a productivity app that provides a streamlined workflow and helps users stay organized and focused."
User Personas
To truly understand your target audience, create detailed user personas. These fictional characters represent your ideal customers and help you empathize with their needs and motivations.
When creating user personas, consider factors such as:
Demographics: Age, gender, location, education, income
Psychographics: Values, beliefs, interests, lifestyle
Goals and motivations: What are their aspirations and what drives their behavior?
Pain points: What challenges or frustrations do they face?
Technology usage: How do they interact with technology?
Below are user personas we created during the product design process for Keyveve, a debt management app. See the full case study here.

User Journey Mapping
A user journey map is a visual representation of a user's interaction with your product from start to finish. It helps you identify pain points, opportunities for improvement, and the overall user experience.
When creating a user journey map, consider the following stages:
Awareness: How did the user first become aware of your product?
Consideration: What factors influenced their decision to choose your product over competitors?
Purchase: How did the user purchase or acquire the product?
Onboarding: What was the user's experience when first using the product?
Usage: How frequently do they use the product and for what purposes?
Loyalty: Are they satisfied with the product and likely to recommend it to others?
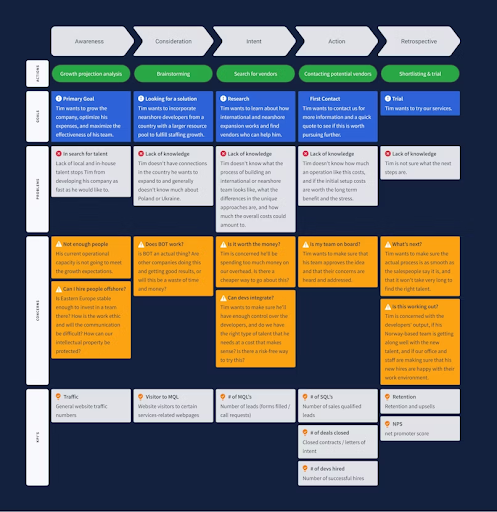
User Experience mapping.
Through users' journeys, you will identify areas where you can improve the product experience and increase customer satisfaction.
Stage 3: Prototyping and Testing
So, you have a clear understanding of the problem and your target audience, it's time to bring your ideas to life. This is where prototyping and testing come into play.
Low-fidelity Prototyping
Low-fidelity prototypes are simple, rough sketches or models that help you visualize your product concept without investing too much time or resources. They can be created using pen and paper, basic design tools, or even physical materials.
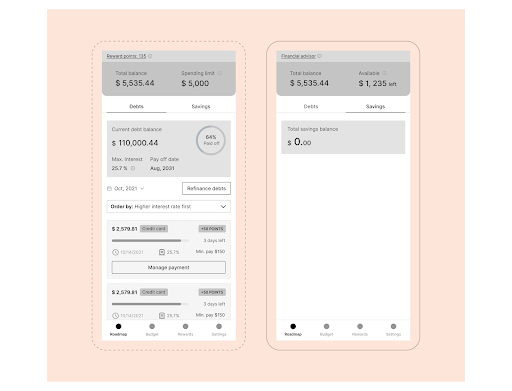
Low-fidelity prototypes for Keyveve.
Benefits of low-fidelity prototyping:
Rapid iteration: Low-fidelity prototypes can be created quickly and easily, allowing you to experiment with different ideas and make changes on the fly.
Early feedback: Testing low-fidelity prototypes with users can help you identify potential issues and gather feedback early in the design process.
Reduced costs: Creating low-fidelity prototypes is generally less expensive than building high-fidelity prototypes or developing a fully functional product.
High-fidelity Prototyping
High-fidelity prototypes are more detailed and realistic representations of your product. They may include interactive elements, visual designs, and functional features.
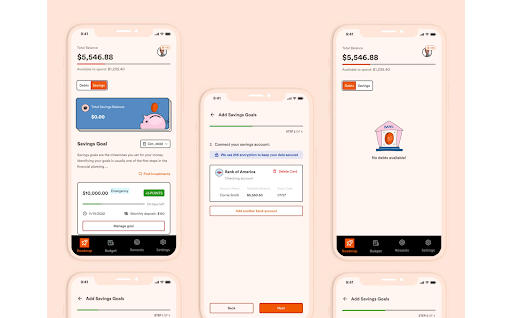
High-fidelity prototypes.
Benefits of high-fidelity prototyping in the product design process:
Enhanced user experience: High-fidelity prototypes can provide a more realistic experience for users, helping you to identify usability issues and gather more accurate feedback.
Improved communication: High-fidelity prototypes can help you communicate your vision to stakeholders and team members more effectively.
Investor attraction: A polished high-fidelity prototype can be a valuable tool for attracting investors and securing funding.
Usability Testing
Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with your prototype and gathering feedback on their experience. This can help you identify usability issues, improve the user experience, and validate your product concept.
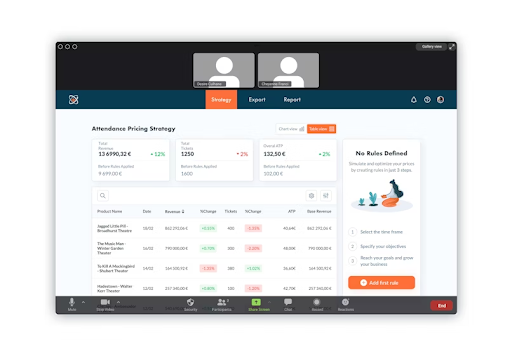
Remote usability testing example.
Key aspects of usability testing:
Recruiting participants: Select participants who represent your target audience and ensure they are representative of the diversity of your user base.
Creating test tasks: Develop tasks that simulate real-world scenarios and allow users to interact with your prototype in a meaningful way.
Observing and recording: Observe users as they complete the tasks and record their actions, comments, and expressions.
Analyzing feedback: Analyze the data collected from usability testing to identify areas for improvement and make necessary changes to your design.
Iterative Design
Product design is an iterative process, which means that it involves continuous refinement and improvement based on feedback.
To make informed decisions, designers must incorporate user feedback and insights from testing.
Key principles of iterative design:
Embrace feedback: Be open to feedback from users, stakeholders, and team members.
Test early and often: Conduct usability testing throughout the design process to identify and address issues early on.
Make small changes: Implement small, incremental changes to your design based on feedback and testing results.
Measure and analyze: Track key metrics to assess the effectiveness of your design changes and make data-driven decisions.
Stage 4: Design Implementation
With a solid foundation of ideas, user research, and prototyping, you may now bring your vision to life through design implementation.
This stage of the product design process involves transforming your concepts into a tangible and functional product.
Design System
A design system is a collection of reusable components, guidelines, and principles that define the look and feel of your product. It ensures consistency, efficiency, and scalability throughout the design and development process.
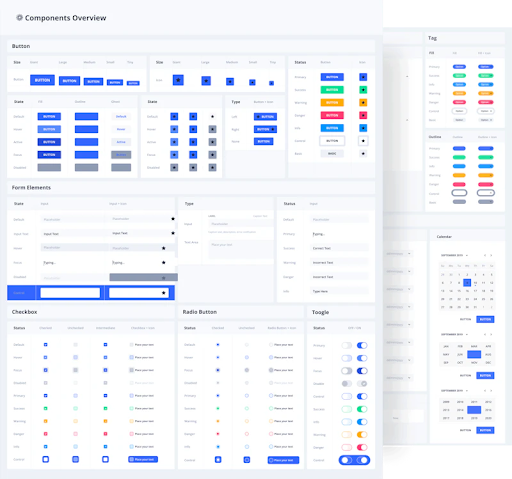
Example of a design system.
Benefits of a design system:
Efficiency: By establishing a set of standardized components and guidelines, you can simplify the design and development process and reduce time-to-market.
Consistency: A design system ensures that your product maintains a consistent look and feel across different platforms and devices.
Scalability: As your product grows, a design system provides a scalable framework that can accommodate new features and functionality.
Collaboration: A design system fosters collaboration between designers, developers, and other stakeholders by providing a shared language and understanding of the product's design principles.
UI/UX Design
User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design are critical components of product development. UI focuses on the visual elements of the product, while UX focuses on the overall user experience.
Why is good UI/UX design important?
User satisfaction: A well-designed UI and UX can enhance user satisfaction and engagement.
Usability: Intuitive interfaces and clear navigation make it easy for users to find what they need and accomplish their goals.
Brand consistency: A cohesive UI and UX can reinforce your brand identity and create a memorable experience for users.
Visual Design
Now, let's get to the really fun part. Visual design plays a huge role in creating aesthetically pleasing and engaging products. It involves selecting colors, typography, imagery, and other visual elements to create a visually appealing and cohesive design.
Key considerations for visual design:
Brand identity: Ensure that your visual design aligns with your brand's personality and messaging.
Readability: Use clear and legible typography that is easy to read on different devices.
Color palette: Choose colors that are visually appealing and evoke the desired emotions.
Imagery: Use high-quality images and graphics that enhance the overall visual appeal of your product.
Accessibility
Designing products that are accessible to people with disabilities is important for ensuring inclusivity and meeting legal requirements.
Accessibility features can include:
Alternative text for images: Provide descriptive text for images to assist users with visual impairments.
Keyboard navigation: Ensure that users can navigate your product using only a keyboard.
Color contrast: Use color combinations that are easily distinguishable for users with color vision deficiencies.
Accessibility guidelines: Adhere to accessibility guidelines such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) to ensure your product meets industry standards.
Stage 5: Launch and Iteration
Congratulations! You've made it to the final stage of the product design process. Now it's time to launch your product and watch it take flight. But how do you go about that? Read on.
Product Launch
Launching a new product requires a well-thought-out strategy to generate excitement and drive adoption.
Here are some key considerations:
Marketing and promotion
Develop a comprehensive marketing plan to reach your target audience and create awareness of your product. Utilize various channels such as social media, content marketing, email marketing, and public relations.
Pricing strategy
Determine a competitive and profitable pricing strategy that aligns with your product's value proposition and target market.
Distribution channels
Choose the appropriate channels to reach your customers, whether it's through your own website, app stores, or partnerships with retailers.
Public relations
Build relationships with media outlets to generate press coverage and create buzz around your product.
Post-Launch Evaluation
Once your product is launched, it's essential to monitor its performance and gather feedback from users. This will help you identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Track UX metrics such as user acquisition, engagement, retention, and customer satisfaction to measure the success of your product.
User Feedback
Collect user feedback through surveys, reviews, and social media to understand their experiences and identify pain points.
Analytics
Use analytics tools to track user behavior, identify trends, and measure the effectiveness of your marketing efforts.
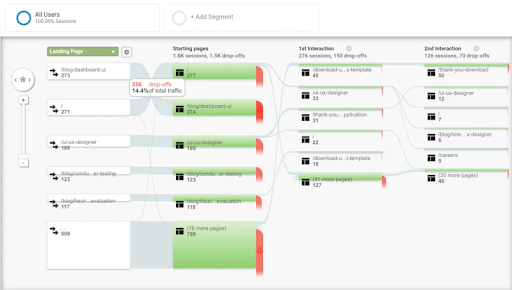
Usage analytics report example.
Continuous Improvement
The product design process is a loop, and it's important to embrace continuous improvement.
Working hard to regularly update and refine your product based on feedback and changing market conditions will ensure its long-term success.
Iterative updates: Regularly release updates to your product based on user feedback and evolving market trends.
Feature prioritization: Use data-driven insights to prioritize new features and improvements that will have the greatest impact on user satisfaction.
A/B testing: Experiment with different design elements and features to identify the most effective approaches.
Customer support: Provide excellent customer support to address user concerns and build customer loyalty.
Conclusion
We've explored the five key stages of the product design process: ideation and research, defining the problem, prototyping and testing, design implementation, and launch and iteration. Embracing these steps through a user-centered approach will lead to creating exceptional digital products that resonate with your target audience.
Well-designed products are how you drive customer satisfaction and loyalty. By investing in product design, you can differentiate your product from the competition and establish a strong brand presence.
Are you ready to embark on your own product design journey? If you're interested in working with an experienced product design team, or simply have questions, don't hesitate to reach out to us.
FAQs
What is the difference between UI and UX design?
UI design focuses on the visual elements of a product, such as layout, color, and typography. UX design, on the other hand, is concerned with the overall user experience, including how easy it is to use the product and achieve goals.
What tools are used in product design?
There are many tools used in product design, including Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch, InVision, and Balsamiq. These tools help designers create prototypes, wireframes, and visual designs.
How can I improve my product design skills?
To improve your product design skills, consider taking online courses, attending workshops, or practicing regularly. Additionally, staying up-to-date with industry trends and best practices can help you stay ahead of the curve.